|
.
.
How many spacecrafts
were launched?
In 1960,
44 spacecrafts were launched, 20 more than the previous year, and 26 more
than the last three years average.
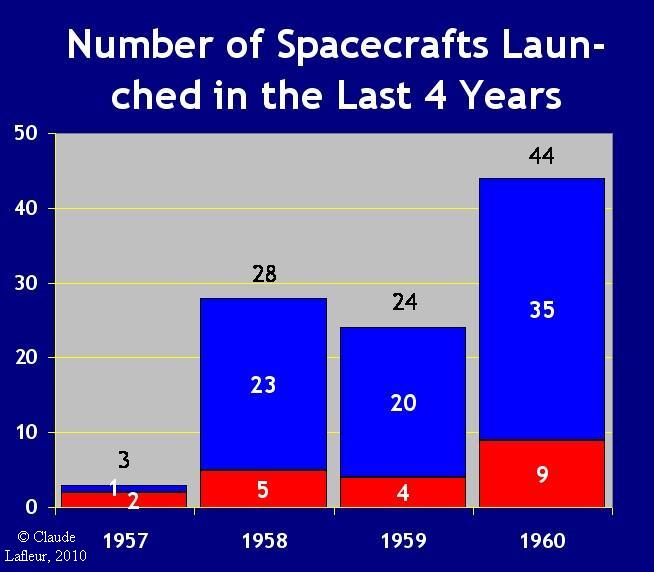
This graph shows that the number of spacecrafts launched
in 1960 nearly doubled those of previous years.
..
For whom these space-
crafts were launched?
....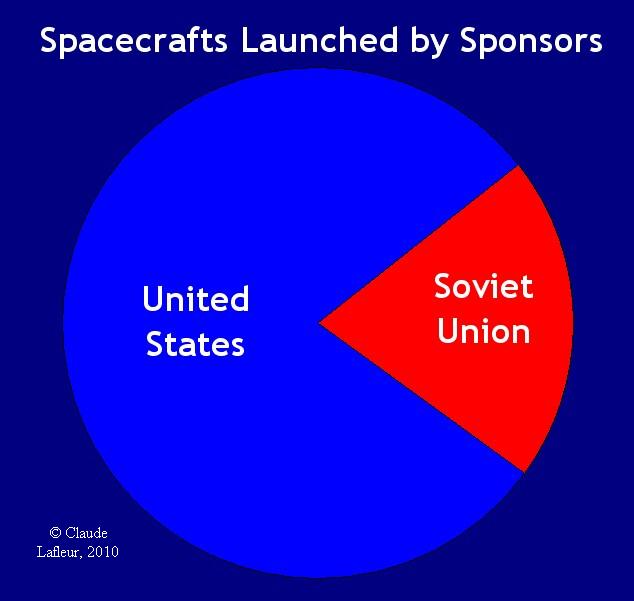
This graph shows that 80% of all
spacecrafts launched in 1960 were American's, and 20% were Soviet's.
..
How many failure had
occured during the year?
| • |
22 launches failed |
| • |
27 satellites were
lost |
In 1960, 55% of all rockets launched
failed, as well as 60% of all spacecrafts. Of those failures,
19 were American’s (in 35 missions) and 8 were Soviet’s (in 9 missions). |
|
.
.
For what purpose 22 civilian spacecrafts were
launched?
.
For what purpose 22 military satellites were
launched?
Note: all military satellites
were launched by the United States (none by the Soviet Union).
.
To which categories are
related these spacecrafts?
| . |
1960 |
Pre-
vious |
Laet
Three |
| Civilian: |
. |
. |
. |
| • Exploration |
18 |
+4 |
+6 |
| • Applications |
4 |
+4 |
+4 |
| • R &
D |
0 |
= |
-1 |
| . |
. |
. |
. |
| Military: |
. |
. |
. |
| • Applications |
13 |
+8 |
+11 |
| • Services |
5 |
+4 |
+5 |
| • R &
D |
4 |
= |
= |
.
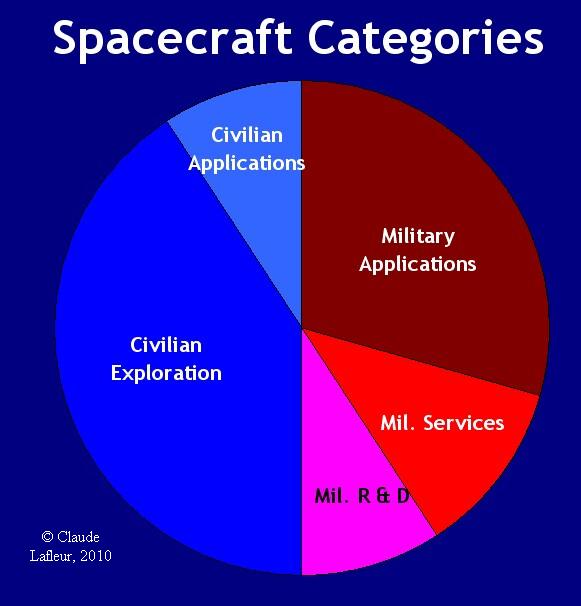 This graph shows that half of the spacecrafts
launched in 1960 were of civilian nature, and the other half for military
purpose.
This graph shows that half of the spacecrafts
launched in 1960 were of civilian nature, and the other half for military
purpose. |
.
..
How many rockets
were launched?
| . |
Number |
Percent |
| Russian |
9 |
22% |
| American |
32 |
78% |
| . |
. |
. |
| Total |
41 |
100% |
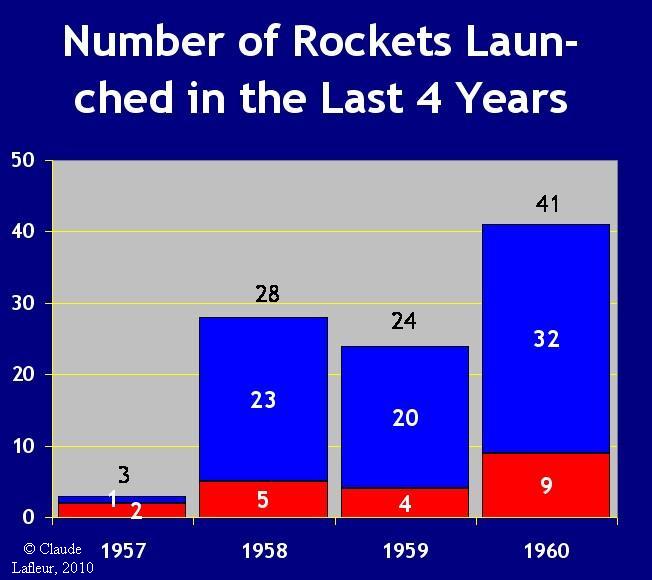
This graph shows that the number of rockets launched
in 1960 nearly double those of previous years.
.
1957-1960 Summary
|
USSR |
USA |
| Sucessful launches |
9 |
35 |
| Failed launches |
11 |
41 |
| Total launches |
20 |
76 |
| Per cent of success |
45% |
46% |
| Mass orbited |
14 tons |
17 tons |
This table shows that, after four years of space activities,
the Soviet Union and the United States had the same success rate in launching
their payloads (45%) and had launched about the same tonnage (14/17 tons).
But the USA had launched nearly four times as much spacecraft than the
USSR. (See Launcher
and Payload Scoreboard below.)
.
How many rockets were launched compared
to previous years?
.
| . |
1960 |
Pre-
vious |
Last
Three |
| Russian |
9 |
+5 |
+5 |
| American |
32 |
+12 |
+17 |
| . |
. |
. |
. |
| Total |
41 |
+17 |
+23 |
Explanation:
“In 1960, the United States launched 32 rockets, 12 more than the previous
year, and 17 more than the last three years average.”
.
Which countries laun-
ched these spacecrafts?
| . |
Number |
Percent |
| Russia |
9 |
20.5% |
| U.S.A. |
35 |
79.5% |
| . |
. |
. |
| Total |
44 |
100% |
Explanation:
“In 1960, the United States launched 35 of the 44 spacecrafts, or 80%,
launched that year."
.

This graph shows that 80% of all spacecrafts launched
in 1960 were made by American rockets.
|
