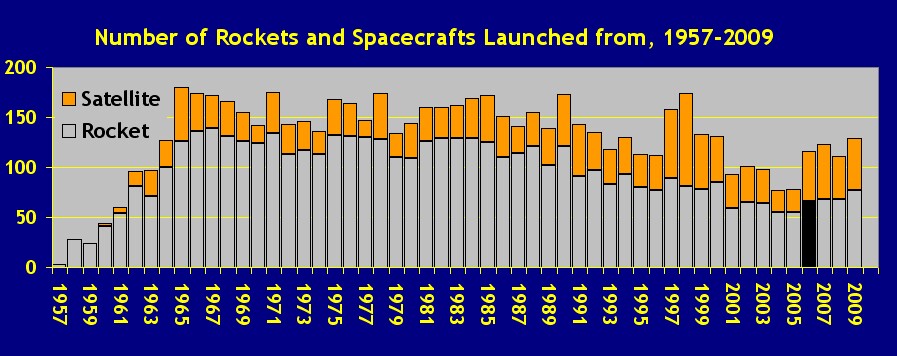
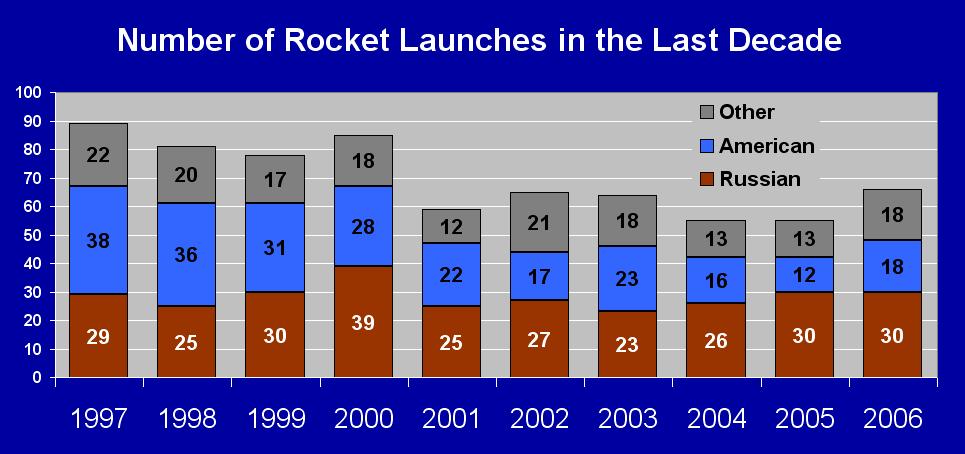
A Good Year
In 2006, 116
spacecrafts were launched. This represents the best year since 2000 (when
131
spacecrafts were launched). From 1964 to 2000, an average of 155 spacecrafts
were launched each year, but there were only 93
spacecrafts launched in 2001, 101
in 2002,
98 in 2003, 77
in 2004 and 78 in 2005. (See
Table
1 - Numbers of Spacecrafts Launched Each Year.)
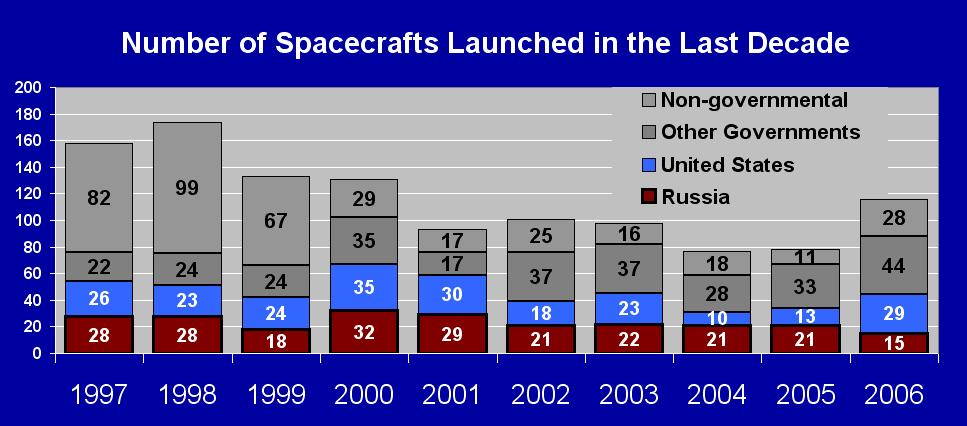
In 2006,
we observed that:
| |
Russia launched the greatest number of rockets (30
of the 66) and of spacecrafts (50 of the 116 payloads),
as it did in 2005. |
| |
The United States launched 50% more rockets (18
compared to 12 in 2005) and more than
double its amount of payloads (37 compared to 14
in 2005). |
| |
Japan launched a record number of national satellites
(11). |
| |
Europe and China launched about the same number of satellites
(respectively 11 and 7) as they did
in 2005. |
| |
The were a record number of small satellites launched:
22 weight less than ten kilograms as another 16 weight less than 100 kg.
These 38 spacecrafts represent a third of all payloads launched in 2006
but less than 1% of the total mass launched. (See 2006 Payloads
Weights Orbited below.) |
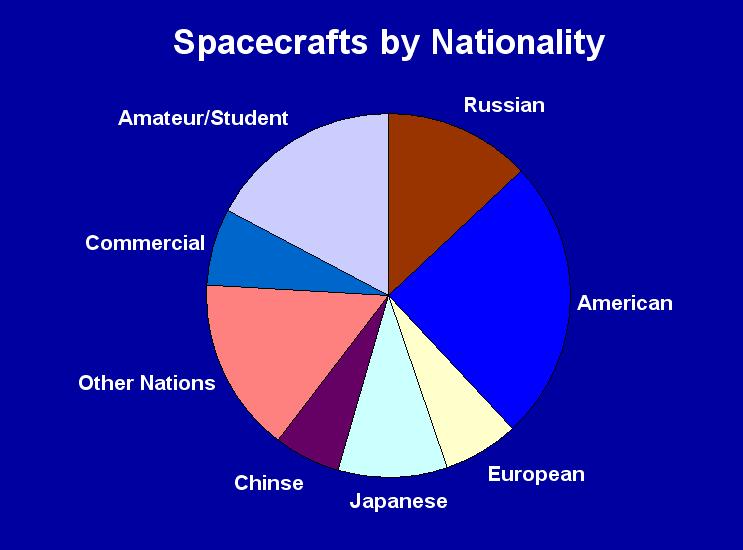
Who Sponsored What?
| Of the 116
spacecrafts launched this year, 29
were American, 15 were Russian, 11
Japanese, 8 European, 8
commercial, 7 Chinese, 6
Taiwenese and there were 20 amateur/student-built
minisatellites. There were also 2 Arab and
2
South Korean satellites, as well as 1
Indian, 1 Israelian, 1
Mexican, 1 Australian, 1
Thailandese and 1 Malaysian. Also in 2006,
Kazakhstan
and Bellarus orbited their first satellite. |
 |
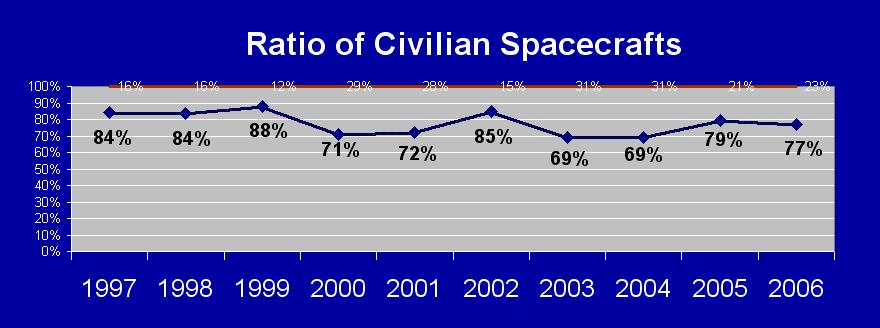
Civilian vs. Military Spacecrafts
89
of the 116 spacecrafts launched
during 2006 were civilian which represents 76.7 % of the total and
27
were military satellites. From 1960 to 1990, two-third of all spacecrafts
launched were military, but since 1995, the majority are civilian. Nevertheless,
54.25 % of all spacecrafts ever launched are military. (See
Table
4.)
For What Purpose?
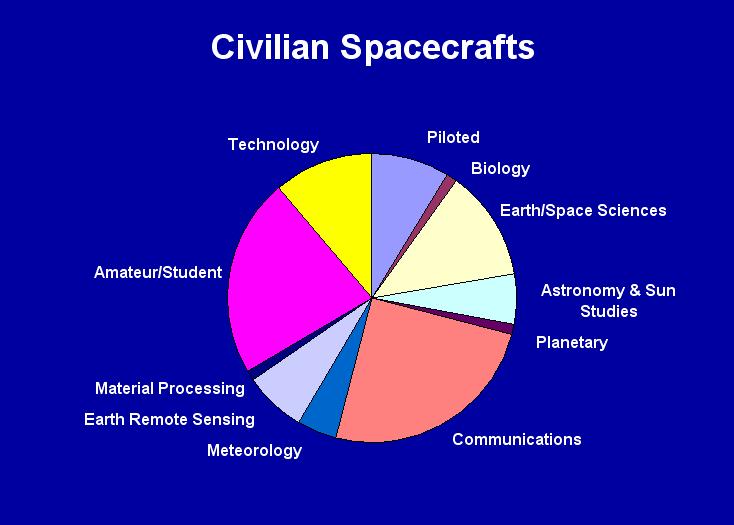
| Of the
89
civilian spacecrafts, 22 provided
communications services, 10 were
for technology R&D, 8 were part
of piloted programs, 11 studied Earth
and space environment, 1 explored
the Solar System and 5 observed
the Universe and our Sun. There were also 4
satellites for weather monitoring, 6
for Earth remote sensing, 1 for
material processing,
1 for biological
research as well as 20 who were built
by students. |
 |
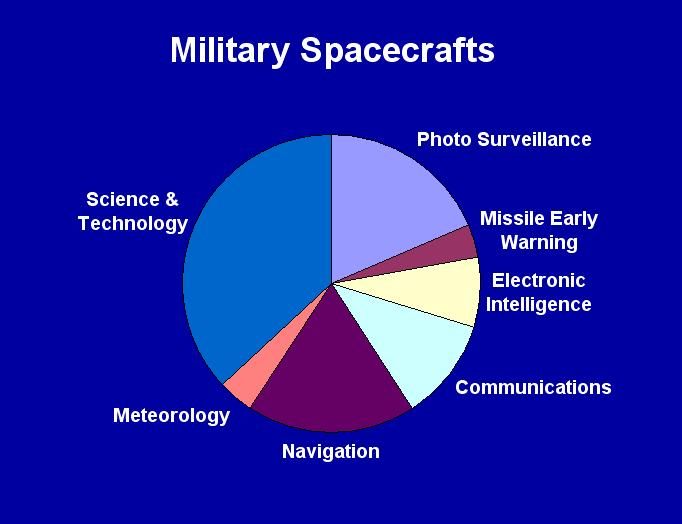
| Of the
27
military satellites, 5 were
for photo surveillance (spy) mission, 5
provided navigation aids, 2 were listening
devices (elint), 3 relayed communications,
1
provide missile early warning, 1
meteorological monitoring and
10
were for science & technology research. |
 |
Space Failures
23
of the 116 spacecrafts failed
to accomplish their mission (18 small satellites were lost on a single
Dnepr
launch). This represents a 80% rate of success, which is far less than
the historical average (1957-2004 = 89.1%). Of these 23 failures, 20 occurred
at launch, one was put in a wrong orbit (Arabsat
4A) and two failed shortly after reaching orbit (Kompass-2
and Sinosat-2). (See Table
6 and Spacecrafts (know) Failure.)
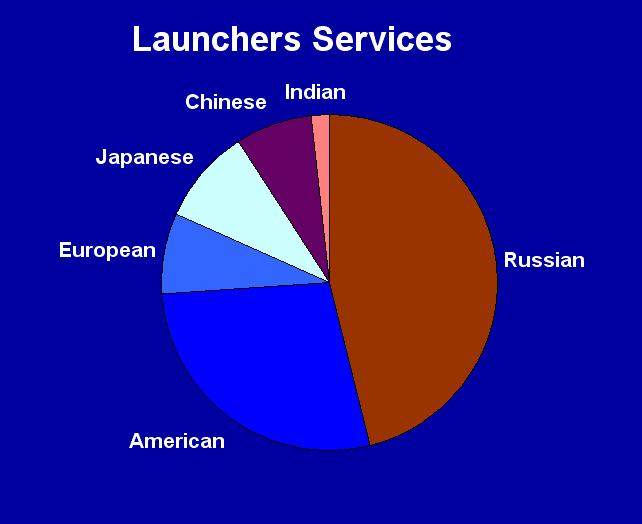
Launcher Statistics
The 116
spacecrafts launched during 2006 were carried by 66
rockets. 30 of which were Russian (45½%),
18
were American, 6 were Japanese,
6 were
Chinese,
5 were European and
1 was
Indian. (See Spacecrafts/Launches Summary below.)
 |
|
Come Fly With Us
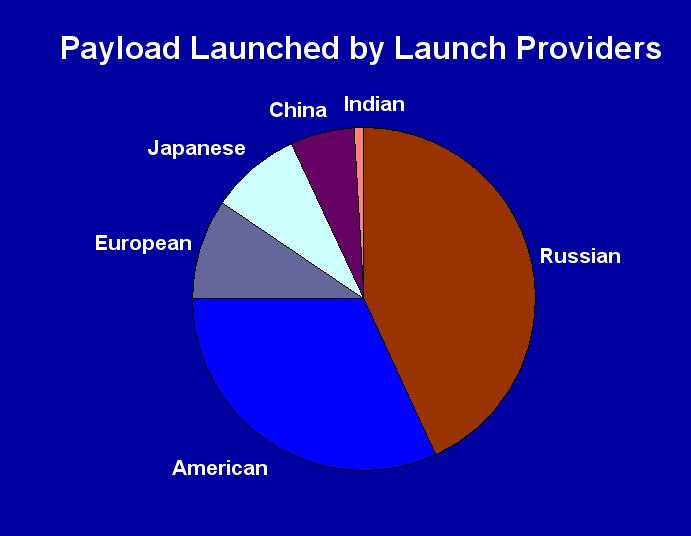
| Russian rockets
launched 50 of the 116
spacecrafts (42%), American rockets carried 37 spacecrafts,
European Ariane orbited 11 spacecrafts, Japanese launchers
H-II and M-V carriee 10 payloads, Chinese Chang Zheng
propelled 7 spacecrafts, as the Indian GSLV transported
1
spacecrafts. |
 |
Payloads Tonnage
Some 256 tons of payloads were
put into space during 2006. Of this, Russia orbited nearly half of the
tonnage, United States a quarter, Europe 15%, as Japan and China orbited
5 to 6% and India none (see table at right).
If we add the weight of the
three Space Shuttle Orbiters flown by NASA, the total tonnage orbited more
than double (to 574 tons) and then the United States would be credited
for orbiting the two-thirds of this mass.
See 2006 Payloads
Weights Orbited below. |
| Launch Provider |
Number of Payloads |
Total Weight Orbited |
% of
Total |
| Russia |
50 |
116½ tons |
45 % |
| United States |
37 |
72 tons* |
28 % |
| Europe |
11 |
39 tons |
15 % |
| Japan |
10 |
14½ tons |
6 % |
| China |
7 |
14 tons |
5½ % |
| India |
1 |
0 tons |
0 % |
| Total |
|
256 tons |
|
Lost Payloads
(at launch) |
20 |
2,3 tons |
|
* Not counting the 318 tons orbited as three Space Shutlle Orbiters |
Launch Failures
There were
4 launch failures: a Dnepr (carrying 18 small
satellites), a Falcon-1, a GSLV
and a Proton (which failed to propelled
Arabsat
4A into geostationary orbit). This represents a 94% rate of success,
which is better than the average 91.5 % success cumulated from 1957 to
2005. (See Table 11 - Launchers
Ranking.)
Launcher Scorecard
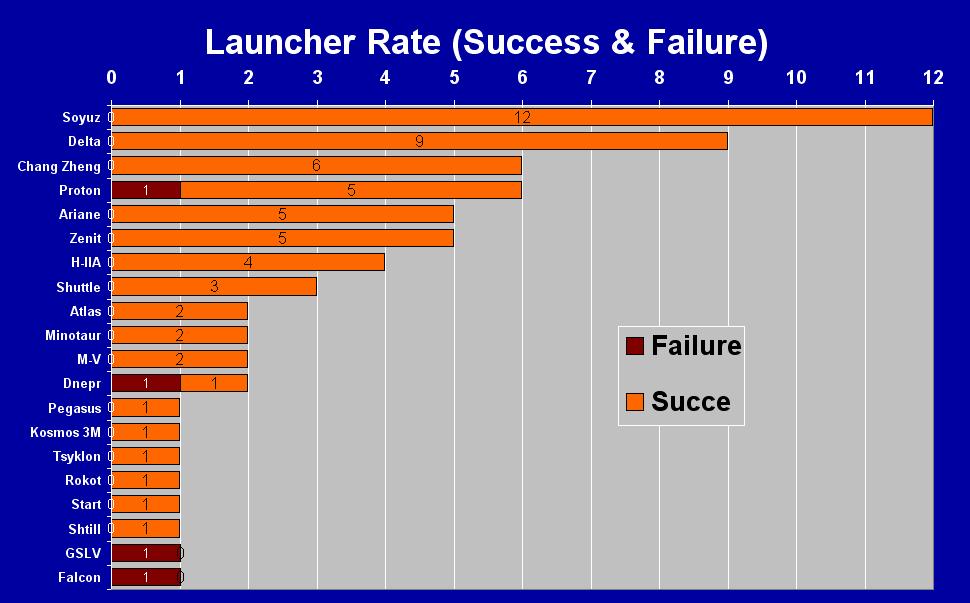
Of the 66
launches accomplished during 2006:
| |
The Russian Soyuz
launcher score 12 successes in 12 launches. |
| |
The American Delta score
9 successes in 9 launches. |
| |
The Chinese Chang Zheng
score 6 successes in 6 launches. |
| |
The Russian Proton score
5 successes in 6 launches. |
| |
The European Ariane and
the Russian
Zenit each score 5 successes in
5 launches. |
| |
The Japanese H-2A
score 4 successes in 4 launches. |
| |
The American Space Shuttle
score 3 successes in 3 launches. |
| |
American Atlas and Minotaur
launchers as well as the Japanese M-V score 2 successes
in 2 launches. |
| |
The Russian Dnepr score 1 success
in 2 launches. |
| |
The American Pegagus and Russian's
Kosmos
3M, Tsykon,
Rokot,
Start
and Shtill each score 1 success in 1 launch. |
| |
The Indian GSLV
and the American Falcon each score 1 failure
in 1 launch. |
| Summary of spacecrafts launched
in 2006 |
Spacecrafts by Sponsors and Mission
Categories
.
| Category |
Russia |
United States |
Other
governments |
Non-governemental
(Commercial/Amateur) |
| CIVILIAN |
|
. |
. |
. |
| Exploration: |
. |
. |
. |
. |
|
Piloted
Programs: |
Soyuz TMA-8 / ISS 12S,
Progress M-56 / ISS 21P,
Progress
M-57 / ISS 22P,
Soyuz TMA-9
/ ISS 13S,
Progress
M-58 / ISS 23P |
STS-121 / ULF-1.1,
STS-115 / ISS
12A,
STS-116 / ISS
12A.1 |
. |
. |
|
Earth/Space
Sciences: |
Kompass-2 (Compas-2), |
CloudSat |
Formosat-3 FM1,
Formosat-3 FM2,
Formosat-3 FM3,
Formosat-3 FM4,
Formosat-3 FM5,
Formosat-3 FM6,
CALIPSO,
SJ-6-2A / Shi
Jian 6-2A,
SJ-6-2B / Shi
Jian 6-2B |
. |
|
Biology: |
. |
Genesat-1 |
. |
. |
|
Astronomy: |
. |
. |
ASTRO-F / Akari,
SOLAR-B / Hinode,
STEREO Ahead,
STEREO
Behind,
COROT |
. |
|
Planetary
Exploration.: |
. |
New Horizons, |
. |
. |
| Applications: |
. |
. |
. |
. |
|
Communications |
Meridian 1
(Meridian N1) |
. |
Arabsat 4A / BADR-ONE,
Hot Bird 7A,
JCSAT-9,
Satmex 6,
Thaicom 5,
KazSat 1,
Insat 4C,
Hot Bird 8,
JCSAT-10,
Koreasat 5
/ Mugunghwa 5,
Optus D1,
Xinnuo-2 / Sinosat-2,
Badr 4 (Arabsat
4B),
Measat 3 |
EchoStar X / Echostar 10,
Astra 1KR,
Galaxy 16,
DirecTV 9S,
XM 4 Blues / XM
Radio 4,
WildBlue 1,
AMC 18 |
|
Meteorology: |
. |
GOES-13 / GOES
N |
MTSAT 2,
METOP A,
Fengyun 2D |
. |
| ,Earth
Remote sensing/imaging: |
Resurs-DK1 |
. |
ALOS / Daichi,
Eros-B / Eros-B1,
Yaogan 1 / RSS 1,
BelKA,
KOMPSAT-2 /
Arirang-2S, |
. |
| Materials
processing: |
. |
. |
SJ-8 / Shi Jian
8 |
. |
| Amateur-student |
. |
. |
. |
RadioSkaf /(SuitSat)
AMSAT-OSCAR 54 (AO-54),
Cute 1.7 + APD,
Baumanets,
Unisat-4,
PICPOT,
ICECube-1,
ION,
RINCON,
AeroCube-1,
CalPoly CP1,
SEEDS,
nCube-1,
HAUSAT-1,
MEROPE,
CalPoly CP2,
KUTESat,
SACRED,
Voyager,
ICECube 2,
HIT-SAT |
| Technology:. |
. |
ST5-A (ST5-FWD),
ST5-B (ST5-MID),
ST5-C (ST5-AFT),
ITS-P3/P4,
ITS-P5 |
SSP / "Solarsail Sub Payload",
SSSAT,
LDREX-2,
ETS-8 / Kiku 8 |
Genesis 1, |
| MILITARY |
. |
. |
. |
. |
| Applications: |
. |
. |
. |
. |
|
Photo
Surveillance: |
Kosmos 2420 / Kobal't-M 2,
Kosmos 2423
/ Don |
NROL-21 (USA
193) |
IGS Optical-2,
SAR-Lupe 1 |
. |
|
Early
Warning: |
Kosmos 2422
/ Oko, |
. |
. |
. |
|
Electronic
Intelligence: |
Kosmos 2421
/ US-PU |
NROL-22 (USA
184) |
. |
. |
|
Ocean surveillance: |
. |
. |
. |
. |
| Services: |
. |
. |
. |
. |
|
Communications: |
. |
. |
Spainsat,
Syracuse
3B,
ZX-22A /
Zhongxing-22A |
. |
|
Navigation: |
Kosmos 2424
/ Uragan,
Kosmos 2425
/ Uragan,
Kosmos 2426
/ Uragan |
Navstar 58
(USA 190),
Navstar 59
(USA 192) |
. |
. |
|
Meteology: |
. |
DMSP Block
5D-3 F-17 (USA 191) |
. |
. |
|
Radar
calibration: |
. |
. |
. |
. |
| War-in-space: |
. |
. |
. |
. |
| Sciences & Technologies: |
.. |
FalconSat 2,
MITEx (USA 187),
MITEx (USA 188),
MITEx (USA 189),
MEPSI 2A/2B,
RAFT-1,
NMARS,
ANDE-MAA,
ANDE-FCAL,
TacSat 2 |
. |
. |
|
.
Launchers / Spacecrafts Summary
..
|
Launcher |
|
Payloads |
| 12 |
Soyuz: |
|
Soyuz TMA-8 |
|
|
|
Progress M-56 |
|
|
|
Kosmos 2420 / Kobal't-M
2 |
|
|
|
Resurs-DK1 |
|
|
|
Progress M-57 / ISS 22P |
|
|
|
Kosmos 2422 / Oko |
|
|
|
Kosmos 2423 / Don |
|
|
|
Soyuz TMA-9 / ISS 13S |
|
|
|
METOP A |
|
|
|
Progress M-58 / ISS 23P |
|
|
|
Meridian 1 (Meridian N1) |
|
|
|
COROT |
| 6 |
Proton: |
|
(Arabsat 4A) |
|
|
|
KazSat 1 |
|
|
|
Hot Bird 8 |
|
|
|
Badr 4 (Arabsat 4B) |
|
|
|
Measat 3 |
|
|
|
Kosmos 2424 / Uragan,
Kosmos 2425 / Uragan,
Kosmos 2426 / Uragan |
| 5 |
Zenit: |
|
EchoStar X |
|
|
|
JCSAT-9 |
|
|
|
Galaxy 16 |
|
|
|
Koreasat 5 |
|
|
|
XM 4 Blues / XM Radio 4 |
| 2 |
Dnepr: |
|
Genesis 1 |
|
|
|
(BelKA),
(Baumanet(),
(Unisat-4 ),
(PICPOT),
(ICECube-1),
(ION),
(RINCON),
(AeroCube-1),
(CalPoly CP1),
(SEEDS),
(nCube-1),
(HAUSAT-1),
(MEROPE),
(CalPoly CP2),
(KUTESat),
(SACRED),
(Voyager),
(ICECube 2), |
| 1 |
Kosmos 3M: |
|
SAR-Lupe 1 |
| 1 |
Tsyklon: |
|
Kosmos 2421 / US-PU |
| 1 |
Rokot: |
|
KOMPSAT-2 |
| 1 |
Start: |
|
Eros-B / Eros-B1 |
| 1 |
Shtill: |
|
Kompass-2 (Compas-2) |
| 1 |
"Handheld" |
|
RadioSkaf |
.
N.B. :Spacecraft in parentheses () were loss at launch. |
|
Launcher |
|
Pahload |
| 9 |
Delta: |
|
CALIPSO,
CloudSat |
|
|
|
GOES-13 / GOES N |
|
|
|
MITEx (USA 187),
MITEx (USA 188),
MITEx (USA 189) |
|
|
|
NROL-22 (USA 184) |
|
|
|
Navstar 58 (USA 190) |
|
|
|
STEREO Ahead,
STEREO Behind |
|
|
|
DMSP Block 5D-3 F-17 (USA
191) |
|
|
|
Navstar 59 (USA 192) |
|
|
|
NROL-21 (USA 193) |
| 3 |
Space Shuttle: |
|
STS-121 / ULF-1.1 |
|
|
|
STS-115 / ISS 12A,
ITS-P3/P4 |
|
|
|
STS-116 / ISS 12A.1,
ITS-P5,
MEPSI 2A/2B,
RAFT-1,
NMARS,
ANDE-MAA,
ANDE-FCAL |
| 2 |
Atlas: |
|
New Horizons |
|
|
|
Astra 1KR |
| 2 |
Minotaur: |
|
Formosat-3 FM1,
Formosat-3 FM2,
Formosat-3 FM3,
Formosat-3 FM4,
Formosat-3 FM5,
Formosat-3 FM6 |
|
|
|
TacSat 2,
Genesat-1 |
| 1 |
Pegasus: |
|
ST5-A (ST5-FWD),
ST5-B (ST5-MID),
ST5-C (ST5-AFT) |
| 1 |
Falcon: |
|
(FalconSat 2) |
.
.
.
|
.
2006 Payloads Weights Orbited
.
|
Russian-launched
|
American-launched
|
European-launched
|
| Payloads |
W. (kg) |
| RadioSkaf |
~50 |
| EchoStar X |
4,333 |
| Arabsat 4A |
3,300 |
| Soyuz TMA-8 |
7,220 |
| JCSAT-9 |
4,401 |
| Progress M-56 |
7,450 |
| Eros-B / Eros-B1 |
360 |
| Kosmos 2420 |
6,700 |
| Kompass-2 |
80 |
| Resurs-DK1 |
6,650 |
| KazSat 1 |
1,400 |
| Galaxy 16 |
4,640 |
| Progress M-57 |
7,450 |
| Kosmos 2421 |
3,150 |
| Genesis 1 |
1,300 |
| Kosmos 2422 |
1,750 |
| BelKA |
750 |
| Baumanets |
(92) |
| Unisat-4 |
(12) |
| PICPOT |
(2) |
| ICECube-1 |
(1) |
| ION |
(2) |
| RINCON |
(1) |
| AeroCube-1 |
(1) |
| CalPoly CP1 |
(1) |
| SEEDS |
(1) |
| nCube-1 |
(1) |
| HAUSAT-1 |
(1) |
| MEROPE |
(1) |
| CalPoly CP2 |
(1) |
| KUTESat |
(1) |
| SACRED |
(1) |
| Voyager |
(1) |
| ICECube 2 |
(1) |
| KOMPSAT-2 |
800 |
| Hot Bird 8 |
4,875 |
| Koreasat 5 |
4,500 |
| Kosmos 2423 |
6,750 |
| Soyuz TMA-9 |
7,220 |
| METOP A |
4,093 |
| Progress M-58 |
7,450 |
| XM 4 Blues |
5,200 |
| Badr 4 (Arabsat 4B) |
3,304 |
| Measat 3 |
4,765 |
| SAR-Lupe 1 |
720 |
| Meridian 1 |
~1,000 |
| Kosmos 2424 |
1,480 |
| Kosmos 2425 |
1,480 |
| Kosmos 2426 |
1,480 |
| COROT |
650 |
| Total orbited: |
116,511 |
|
| Payloads |
W. (kg) |
| New Horizons |
450 |
| ST5-A |
25 |
| ST5-B |
25 |
| ST5-C |
25 |
| FalconSat 2 |
(26) |
| Formosat-3 FM1 |
62 |
| Formosat-3 FM2 |
62 |
| Formosat-3 FM3 |
62 |
| Formosat-3 FM4 |
62 |
| Formosat-3 FM5 |
62 |
| Formosat-3 FM6 |
62 |
| Astra 1KR |
4,300 |
| CALIPSO |
587 |
| CloudSat |
848 |
| GOES-13 |
3,209 |
| MITEx (USA 187) |
250 |
| MITEx (USA 188) |
250 |
| MITEx (USA 189) |
~500 |
| NROL-22 (USA 184) |
4 500 |
| STS-121 payloads |
14,594 |
| STS-115 payloads |
18,481 |
| ITS-P3/P4 |
[15,821] |
| Navstar 58 (USA 190) |
2,032 |
| STEREO Ahead |
620 |
| STEREO Behind |
620 |
| DMSP Block 5D-3 F-17 (USA
191) |
1,154 |
| Navstar 59 (USA 192) |
2,032 |
| STS-116 payloads |
12,523 |
| ITS-P5 |
[1,860] |
| MEPSI 2A/2B |
[3] |
| RAFT-1 |
[4] |
| NMARS |
[3] |
| ANDE-MAA |
[50] |
| ANDE-FCAL |
[75] |
| NROL-21 (USA 193) |
~4,500 |
| TacSat 2 |
370 |
| Genesat-1 |
7 |
| Total orbited: |
72,214 |
Space Shuttle Orbiter
(weight minus payloads)
| Orbiter |
W. (kg) |
| STS 121 |
106,499 |
| STS 115 |
103,918 |
| STS 116 |
107,892 |
| Subtotal |
318,309 |
| Total orbited: |
318,309 |
|
| Payloads |
W. (kg) |
| Hot Bird 7A |
4,100 |
| Spainsat |
3,680 |
| Satmex 6 |
5,300 |
| Thaicom 5 |
2,800 |
| JCSAT-10 |
4,080 |
| Syracuse 3B |
3,750 |
| DirecTV 9S |
5,535 |
| Optus D1 |
2,299 |
| LDREX-2 |
211 |
| WildBlue 1 |
4,735 |
| AMC 18 |
2,081 |
| Total orbited: |
38,614 |
| Payloads |
W. (kg) |
| Insat 4C |
(2,168) |
| Total orbited: |
0 |
|
Weights in parentheses () are not counted since the spacecraft failed to
reach orbit. Weights in brackets [] are included in the total payload weight
carried by an Orbiter. |